Passing the due date without the symptoms of much-awaited labor will put you in a confused and anxious situation.
Passing the due date without the symptoms of much-awaited labor will put you in a confused and anxious situation.
A pregnant woman focusses on her due date with lots of anticipation and anxiety, especially during the last month of your pregnancy.
However, you should avoid unnecessary anxiety as it is quite usual to deliver one or two weeks prior or until two weeks after the proposed due date. Overdue pregnancy is also known as post-term pregnancy.
When Is A Baby ‘Overdue’?
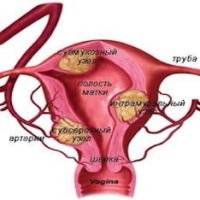
Generally, babies are born between 32 and 42 weeks of gestation. The deliveries during this period are called ‘on term delivery’ or normal pregnancy.
Those babies born before the 37th week is known as preterm or premature babies. When the pregnancy passes 42 weeks, it is known as overdue pregnancy and the babies born are called post-term babies.
How Does One Arrive On A Due Date In Pregnancy?
Usually, the 40 weeks of gestation is calculated from the first day of the last menstrual period of the mother. As the ovulation occurs only around the 14th day of menstruation, the baby will be two weeks younger that she is calculated to be. This little confusion can reflect in the possible inaccuracy of the due date. So, a supposedly overdue baby need not be an actually overdue baby.
How Does A Post-term Pregnancy Occur?
There are several reasons that lead to post-term pregnancy, some of which are enslisted below:
- Miscalculating the due date: The accuracy of the due date depends up on how regular your menstrual cycle is. Getting periods on every 28th day indicate that you have a perfect menstrual cycle. But, if you have an irregular menstrual cycle, the calculation of the ovulation and conception can fail. This can cause miscalculating. the due date. This inaccuracy in estimating the due date can be a major cause of the post-term pregnancy
- First-time mothers: It is said that the first one usually comes late. The main reason behind this can be the first time mother will be well nourished and will take more than enough rest.
- The position of the baby: The position of the baby can affect the start of the labor. When the baby is ‘breech position‘ (with the bottom first position), the labor is found to start slower.
- Previous overdue pregnancy: If your previous pregnancy was overdue, there are chances of passing the due date without any symptoms of labor in your subsequent pregnancies.
- Climate: It is a very curious and strange fact that the pregnancies in summer tend to be longer than the pregnancies in winter.
- Maternal Obesity: Compared to normal-weight women, the risk of longer gestation among obese women is longer.
- Family history: When there are post-term pregnancies run in the family the chances of you having the post-term pregnancy increases.
What Are The Health Risks Associated With Post-Term Pregnancy?
There are numerous dangerous health risks (both maternal and fetal complications) are associated with post-term pregnancy. Some of the health risks are:
- Increased chances of fetal macrosomia: Fetal macrosomia is a condition in which the baby weight weigh more than four kilograms. Fetal macrosomia can squeeze the baby in the birth canal bringing out birth injuries, or increase the chances of assisted delivery using a forceps or vacuum extractor. The chances of uterine ruptures, genital tract lacerations, and excessive bleeding after delivery also increases with the size of the baby.
- Decline in placental function: When the pregnancy passes 41 weeks, the placental function can get decrease and become inadequate, hindering the supply of vital nutrients and oxygen to the fetus (placental insufficiency). The aging of placenta effects the baby’s ability to develop well in the uterus. This will affect the health of the fetus.
- Cerebral palsy: When compared with 40 weeks of gestation, the pregnancy that passed 42 weeks has been associated with an elevated risk of cerebral palsy.
- Placental sulfatase deficiency: This condition arises due to some enzyme defects that occur in the placenta. Women with this condition hardly enter into spontaneous labor.
- Meconium aspiration: The chances of inhaling the fecal waste which leads to breathing problems or infection in the new born increases when the baby is overdue.
What To Do When Your Baby Is Overdue?
Once you go over due on your pregnancy certain measures should be taken to prevent some possible risks. Some of the precaution measures include:
- Counting fetal movements: When the due date is passed, the infant should be monitored closely. A healthy baby often moves frequently. When the baby is unwell the number of the movements tend to decrease. Counting the fetal movements is a simple way to ensure the well being of the child.
- Monitoring the baby with CTG (non-stress test): Monitoring the baby’s heart rate with cardiotocograph is used to ensure the health of the baby. What you should remember is that the CTG result only indicates the health of the baby at the point of time CTG taken. This result should not be mistaken as the prediction of the health of the baby in the future.
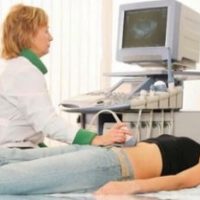
- Monitoring the biophysical profile: A biophysical profile is taken with an ultra sound scan. A biophysical profile can predict the health of the baby better than a non-stress test. Mostly four factors are examined here:
- Baby’s movements.
- Amount of amniotic fluid
- Baby’s muscle tone
- Baby’s breathing
- Amniotic fluid index: The quantity of amniotic fluid is examined with the help of an ultra sound scan. If sufficient amniotic fluid is present, it indirectly indicates that the placenta is functioning properly.
How Is Labor Induced In A Post-Term Pregnancy?
When the pregnancy continues without the signs of labor for more than ten days, then doctors start to concern about the possible complication. Before going into a medically induced labor, some women try to induce the labor naturally by eating certain foods. The methods of Inducing labor medically include:
-
- Membrane sweep: After vaginal examination, the doctor will insert a gloved finger into the cervix and move it to the top of the cervix and the bag of waters in a circular pattern. This will soften the cervix and stimulate the cervix to produce hormones that trigger labor. This increases your chance by 30% for going into labor within 48 hours.
- Administrating Prostaglandin gel: Prostaglandin gel is inserted in the vagina helps in softening the cervix and allow labor to progress naturally.
- Syntocinon drip: An intravenous drip containing the drug Syntocinon is another commonly used method to induce labor. Syntocinon is a synthetic hormone with the qualities of oxytocin, the hormone which has a significant role in the contraction of the womb.
- Breaking the waters: When the cervix is open a couple of centimeters, your doctor will break the water with an instrument shaped like a large crochet hook. This procedure can be quite uncomfortable for the mother. Usually breaking the waters is enough to start the labor.
If not, syntocinon drip is followed to accelerate the labor.
How Is Induced Labor Differ From Natural Labor?
It is found that induced labor can be more painful than a natural labor. Hence, the women who are induced usually ask for an epidural as a pain management technique. It is also found that the women who are induced also have an increased chance of having an assisted delivery.
Actually, about only five per cent of babies will make it on the day they are expected. You should expect the baby to come two weeks prior or two weeks post your due date.
Keep in your mind that, the due date given by your doctor only indicates a possible time for the delivery, not the best time for the delivery. So take some extra rest and relax as your days are about to become very busy as the ‘late comer’ is on his way.